Here is the tutorial about how to scan potential energy over specific internal coordinate (e.g. dihedral angle) ab initio and then transfer this trajectory into molecular mechanics package and compare them.
First of all let’s install all necesarry softwary. At first we need development-branch of MDAnalysis library. Execute following code:
git clone https://code.google.com/p/mdanalysis/ mda cd mda git checkout develop cd package python setup.py build python setup.py install --user
After installing corresponding MNAnalysis version you can convert GAMESS output trajectories from python console or you can use the following script:
#!/usr/bin/python
import MDAnalysis as mda
import sys, getopt, os
try:
opts, args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:], 'i:o:')
except getopt.error, msg:
print 'use ./gms2xyz.py -i <gamess-log> -o <xyz-file>'
sys.exit(2)
infile = None
oufile = None
for o, a in opts:
if o == '-i':
infile = a
elif o == '-o':
oufile = a
if infile == None or oufile == None:
print 'use ./gms2xyz.py -i <gamess-log> -o <xyz-file>'
sys.exit(2)
u = mda.Universe(infile, infile, topology_format='GMS', format='GMS')
xyzw = u.trajectory.OtherWriter(oufile)
xyzw.atomnames = u.atoms.names()
c = 0
u.trajectory.rewind()
print 'Reading: ',
for ts in u.trajectory:
c+=1
ts.dimensions = [50,50,50,90,90,90]
xyzw.write_next_timestep(ts)
print '.',
sys.stdout.flush()
print 'done.\nFrames read: ',c
xyzw.close()
sys.exit(0)
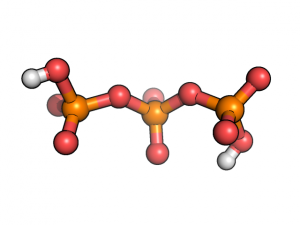
Let’s work with triphosphate molecule protonated at ends:
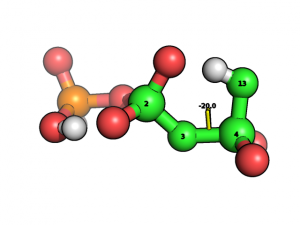
We construct its Z-matrix with help of MOLDEN program and optimizing its geometry in internal coordinates as it discussed here. Then we want to scan potential energy surface over dihedral angle POPO(H):
We found this dihedral in the list of internal coordinates:
$zmat izmat(1)= ... 2, 14, 11, 7, 2, 15, 13, 4, 3, 4, 3, 2 , 1 , 3, 5, 4, 3 , 2 , 3, 12, 4, 3 , 2 , ! this angle 3, 13, 4, 3 , 2 , ! this angle 3, 6, 2, 3 , 4 , 3, 7, 6, 2 , 3 , ... $end
If we want to rotate dihedral angle over 4-3 bond then we should simultaneously rotate over 5-4-3-2, 12-4-3-2 and 13-4-3-2 dihedral angles.� Let this three angles be enumerated as 29,30 and 31 from the first internal coordinate. So the code for scanning over this angle will be the following:
$surf orig1 = 0.0 disp1 = 10.0 ndisp1 = 25 vect1(29) = 1,1,1 $end $contrl ... runtyp=surface ... $end
Here orig1 is the starting value of internal coordinate and zero corresponds to this value in current geometry. disp1 means step of scanning (degrees for angles and Angstroms for bonds). ndisp1 points number of steps in PES scan. vect1 — is array that determines displacement vector in internal coordinates. Notation vect1(a)=b means that vect1 contains all zeroes except at ‘a‘ position where it contains ‘b‘. Correspondingly notation vect1(a)=b,c means that vect1[a]=b and vect1[a+1]=c.
In the end of output file we can find something like this:
------------------------------------ ICOORD1, | COORD1 | ENERGY ---------------+-------------------- 1 ( 110.00000)| -179.8909005836 2 ( 120.00000)| -179.8909024402 3 ( 130.00000)| -179.8792810516 4 ( 140.00000)| -179.8794632800 5 ( 150.00000)| -179.8796675724 6 ( 160.00000)| -179.8797955768 7 ( 170.00000)| -179.8798565530 8 ( 180.00000)| -179.8798748063 9 ( 190.00000)| -179.8798576588 10 ( 200.00000)| -179.8798190243 11 ( 210.00000)| -179.8796941060 12 ( 220.00000)| -179.8796018132 13 ( 230.00000)| -179.8794893926 14 ( 240.00000)| -179.8794119809 15 ( 250.00000)| -179.8793047772 16 ( 260.00000)| -179.8794777600 17 ( 270.00000)| -179.8796382012 18 ( 280.00000)| -179.8868660775 19 ( 290.00000)| -179.8935338430 20 ( 300.00000)| -179.8935018639 21 ( 310.00000)| -179.8935254678 22 ( 320.00000)| -179.8935466698 23 ( 330.00000)| -179.8934722620 24 ( 340.00000)| -179.8935161684 25 ( 350.00000)| -179.8935103932
These are potential energy values for every coordinate.
… to be continued …